What is Carnosine?
Carnosine is a dipeptide composed of the amino acids beta-alanine and histidine, commonly found in muscle and brain tissues. In skincare, carnosine is valued for its antioxidant properties and its ability to protect the skin from glycation, a process where sugar molecules bind to proteins and lipids, leading to the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) that can cause skin aging.
How does this ingredient work in skincare?
As a potent antioxidant, it scavenges free radicals, preventing oxidative damage to skin cells; secondly, it inhibits the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), preserving the structure and function of proteins like collagen and elastin. Carnosine chelates metal ions, further mitigating oxidative stress; fourthly, it modulates inflammatory pathways, reducing redness and irritation. It supports cellular health by promoting DNA repair and delaying cellular senescence.
How does this ingredient compare to others?
Unlike traditional antioxidants such as vitamin C or vitamin E, carnosine possesses specific anti-glycation properties, inhibiting the formation of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs) that contribute to skin aging. Additionally, while some antioxidants focus solely on scavenging free radicals, carnosine's ability to chelate metal ions adds an extra layer of protection against oxidative stress.
In contrast to peptides, which primarily target collagen synthesis or cell signaling pathways, carnosine's diverse mechanisms, including anti-inflammatory effects and cellular support, offer comprehensive skin benefits. Furthermore, compared to retinoids, which can cause irritation and photosensitivity, carnosine provides anti-aging benefits without the risk of adverse reactions, making it suitable for individuals with sensitive skin or those seeking a gentler approach to skincare.
Potential benefits of this ingredient for the skin
Carnosine offers a range of potential benefits for the skin:
- Anti-Aging: Carnosine's antioxidant properties help neutralize free radicals, preventing oxidative damage and reducing the appearance of fine lines, wrinkles, and other signs of aging.
- Skin Firmness and Elasticity: By inhibiting glycation, carnosine helps maintain the structural integrity of proteins like collagen and elastin, promoting skin firmness and elasticity.
- Protection Against Environmental Stressors: Carnosine's ability to chelate metal ions and modulate inflammatory pathways protects the skin from oxidative stress induced by environmental factors such as UV radiation and pollution.
- Reduction of Redness and Irritation: Its anti-inflammatory effects can soothe sensitive or inflamed skin, reducing redness, swelling, and irritation.
- Cellular Health: Carnosine supports cellular repair mechanisms, enhancing cell viability and delaying cellular senescence, which contributes to overall skin health and resilience.
Products we use this ingredient in
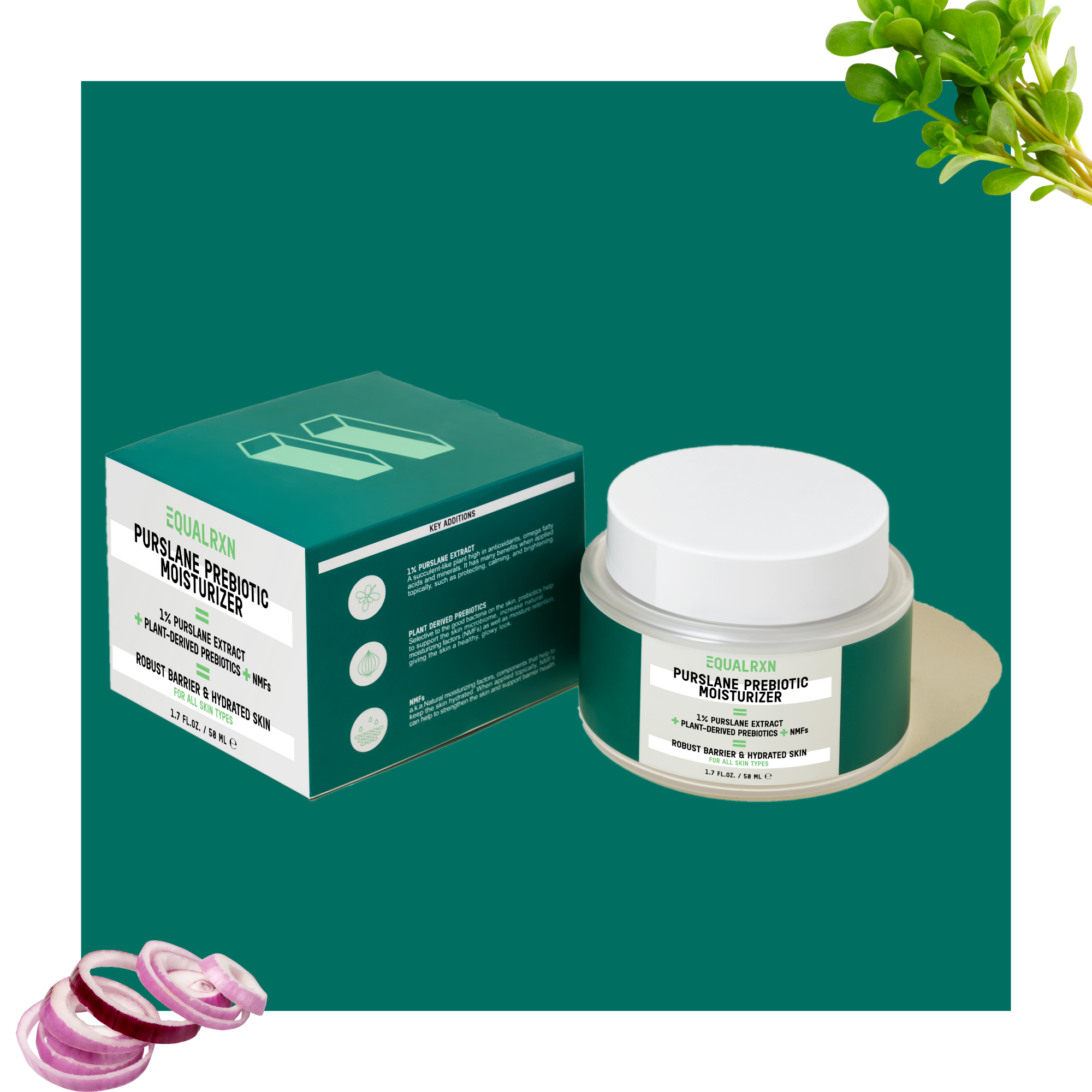
Purslane Prebiotic Moisturizer
References
- Narda, Mridvika et al. “Novel Facial Cream Containing Carnosine Inhibits Formation of Advanced Glycation End-Products in Human Skin.” Skin pharmacology and physiology vol. 31,6 (2018): 324-331. doi:10.1159/000492276
- Babizhayev, Mark A et al. “Skin beautification with oral non-hydrolized versions of carnosine and carcinine: Effective therapeutic management and cosmetic skincare solutions against oxidative glycation and free-radical production as a causal mechanism of diabetic complications and skin aging.” The Journal of dermatological treatment vol. 23,5 (2012): 345-84. doi:10.3109/09546634.2010.521812
- Hipkiss, A R et al. “Carnosine, the anti-ageing, anti-oxidant dipeptide, may react with protein carbonyl groups.” Mechanisms of ageing and development vol. 122,13 (2001): 1431-45. doi:10.1016/s0047-6374(01)00272-x